Table of Contents
ToggleCSS Current Affairs Paper 2016
Paper II
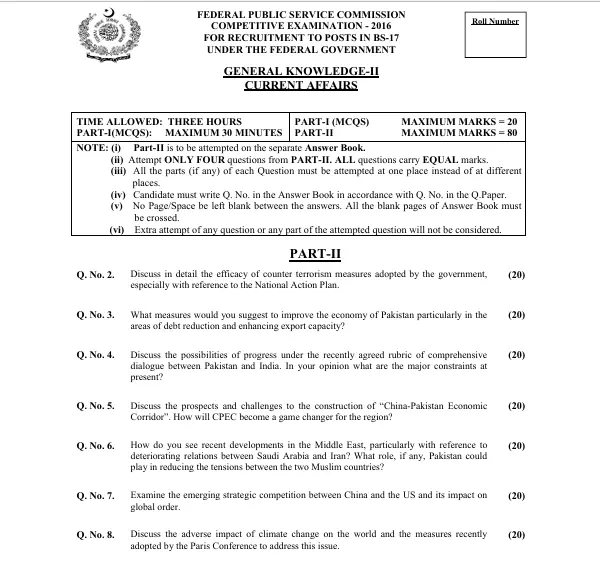
Q. No. 2. Discuss in detail the efficacy of counter-terrorism measures adopted by the government, especially with reference to the National Action Plan.
Q. No. 3. What measures would you suggest to improve the economy of Pakistan, particularly in the areas of debt reduction and enhancing export capacity?
Q. No. 4. Discuss the possibilities of progress under the recently agreed rubric of comprehensive dialogue between Pakistan and India. In your opinion what are the major constraints at present? (20)
Q. No. 5. Discuss the prospects and challenges to the construction of the “China-Pakistan Economic Corridor.”. How will CPEC become a game changer for the region?
Q. No. 6. How do you see recent developments in the Middle East, particularly with reference to deteriorating relations between Saudi Arabia and Iran? What role, if any, Pakistan could play in reducing the tensions between the two Muslim countries?
Q. No. 7. Examine the emerging strategic competition between China and the US and its impact on global order.
Q. No. 8. Discuss the adverse impact of climate change on the world and the measures recently adopted by the Paris Conference to address this issue.
Summary:
Q. No. 2 Discuss in detail the efficacy of counter-terrorism measures adopted by the government, especially with reference to the National Action Plan (NAP).
The National Action Plan (NAP), formulated in 2014, aimed to address terrorism comprehensively in Pakistan. It included 20 points, ranging from eliminating armed militias to curbing hate speech and improving the judicial system for terrorism cases.
Efficacy:
-
-
Military Operations: Operations such as Zarb-e-Azb and Radd-ul-Fasaad significantly weakened militant networks in tribal areas.
-
Control of Hate Speech: Some progress was made in regulating madrassas and curbing extremist propaganda.
-
Improved Security Framework: Establishment of military courts expedited trials of terrorists.
-
Failure in Comprehensive Implementation: However, inconsistent political will and lack of coordination between provinces hindered broader implementation.
-
Lingering Issues: Extremist ideologies and sleeper cells remain persistent challenges.
-
In conclusion, while the NAP reduced terrorism levels significantly, full implementation, especially in addressing root causes, remains critical for long-term success.
Q. No. 3 What measures would you suggest to improve the economy of Pakistan, particularly in the areas of debt reduction and enhancing export capacity?
Debt Reduction:
-
-
Fiscal Discipline: Curtailing unnecessary expenditures and ensuring targeted subsidies.
-
Broadening the Tax Base: Encouraging tax compliance and reducing reliance on indirect taxes.
-
Privatization: Selling non-performing state-owned enterprises.
-
Restructuring Debt: Renegotiating foreign loans and diversifying creditors.
-
Enhancing Export Capacity:
-
-
Value-Added Exports: Focus on processed goods rather than raw materials (e.g., textiles to apparel).
-
Diversification: Expand export portfolios into IT services, engineering goods, and pharmaceuticals.
-
Trade Agreements: Leverage agreements like GSP+ and engage with emerging markets.
-
Ease of Doing Business: Simplify regulations for exporters and provide incentives for innovation.
-
Sustainable policies and investments in industrial capacity are essential to achieve long-term stability and growth.
Q. No. 4 Discuss the possibilities of progress under the recently agreed rubric of comprehensive dialogue between Pakistan and India. In your opinion, what are the major constraints at present?
Possibilities of Progress:
-
-
Trade Relations: Increased trade could reduce hostilities and foster economic interdependence.
-
Confidence-Building Measures (CBMs): Initiatives like people-to-people contact and cultural exchanges could improve relations.
-
Water Sharing Agreements: Strengthening the Indus Water Treaty can address resource disputes.
-
Border Issues: Improved mechanisms to manage LoC violations could build trust.
-
Major Constraints:
-
-
Kashmir Dispute: The core issue continues to impede relations, especially post-abrogation of Article 370 by India.
-
Terrorism Allegations: India’s accusations against Pakistan-based groups hinder dialogue.
-
Political Polarization: Nationalist rhetoric on both sides complicates peace-building efforts.
-
External Influence: Strategic alignments, like India’s partnership with the US and Pakistan’s ties with China, create further divides.
-
To overcome these constraints, a sustained effort focusing on shared interests and regional stability is required.
Q. No. 5 Discuss the prospects and challenges to constructing the “China-Pakistan Economic Corridor” (CPEC). How will CPEC become a game-changer for the region?
Prospects:
-
-
Infrastructure Development: Roads, ports, and energy projects will modernize Pakistan’s economy.
-
Economic Zones: Special Economic Zones (SEZs) under CPEC will attract foreign investment.
-
Regional Connectivity: CPEC could transform Pakistan into a trade hub connecting China, Central Asia, and South Asia.
-
Challenges:
-
-
Security Concerns: Militant threats to CPEC routes and Chinese workers pose risks.
-
Debt Burden: Overreliance on Chinese loans could exacerbate Pakistan’s financial challenges.
-
Local Resistance: Discontent in regions like Balochistan over resource distribution remains unresolved.
-
Geopolitical Tensions: US and Indian opposition to CPEC could lead to diplomatic challenges.
-
CPEC’s success depends on inclusive policies, effective resource allocation, and strategic planning, making it a transformative project for Pakistan and the region.
Q. No. 6 How do you see recent developments in the Middle East, particularly with reference to deteriorating relations between Saudi Arabia and Iran? What role, if any, Pakistan could play in reducing the tensions between the two Muslim countries?
Recent Developments:
-
-
Yemen War: The proxy conflict between Saudi Arabia and Iran continues to escalate.
-
Nuclear Deal: Iran’s strained relations with the West have fueled Saudi concerns.
-
Regional Alliances: Saudi alignment with Israel and Iran’s support for militias like Hezbollah intensify divisions.
-
Pakistan’s Role:
-
-
Mediator: Pakistan can leverage its ties with both nations to mediate dialogue.
-
Neutral Stance: Avoiding taking sides will maintain credibility.
-
Islamic Unity Forums: Utilizing platforms like the OIC to encourage reconciliation.
-
Regional Stability: Supporting confidence-building measures, such as joint anti-terror efforts, could ease tensions.
-
Pakistan’s balanced approach can strengthen its role as a unifying force in the Muslim world.
Q. No. 7 Examine the emerging strategic competition between China and the US and its impact on global order.
Strategic Competition:
-
-
Trade War: Tariffs and economic decoupling signal intensified rivalry.
-
Military Rivalry: Increased presence in the Indo-Pacific reflects security competition.
-
Technological Race: AI, semiconductors, and 5G are focal points of contention.
-
Impact on Global Order:
-
-
Polarization: Countries are forced to choose sides, affecting global alliances.
-
Economic Instability: Disruptions in supply chains and trade flows.
-
New Institutions: Competing global institutions (e.g., AIIB vs. World Bank) challenge US dominance.
-
Geopolitical Shifts: The focus on Asia redefines traditional power centers.
-
This competition may lead to a multipolar world, demanding nuanced diplomacy to avoid escalating tensions.
Q. No. 8 Discuss the adverse impact of climate change on the world and the measures recently adopted by the Paris Conference to address this issue.
Adverse Impact:
-
-
Global Warming: Rising temperatures increase the frequency of extreme weather events.
-
Sea-Level Rise: Threatens coastal cities and small island nations.
-
Food and Water Scarcity: Shifting climate patterns disrupt agriculture.
-
Health Risks: Greater prevalence of diseases like malaria and heat-related illnesses.
-
Paris Conference Measures:
-
-
Emission Targets: Countries agreed to limit global warming to below 2°C.
-
Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs): Each country set voluntary emissions reduction goals.
-
Climate Finance: Developed nations pledged $100 billion annually to support vulnerable countries.
-
Renewable Energy: Emphasis on transitioning to clean energy sources.
-
Despite progress, stronger implementation and accountability mechanisms are necessary to combat the climate crisis effectively.