Table of Contents
ToggleCSS Political Science Paper 2020 (b)
SECTION-A
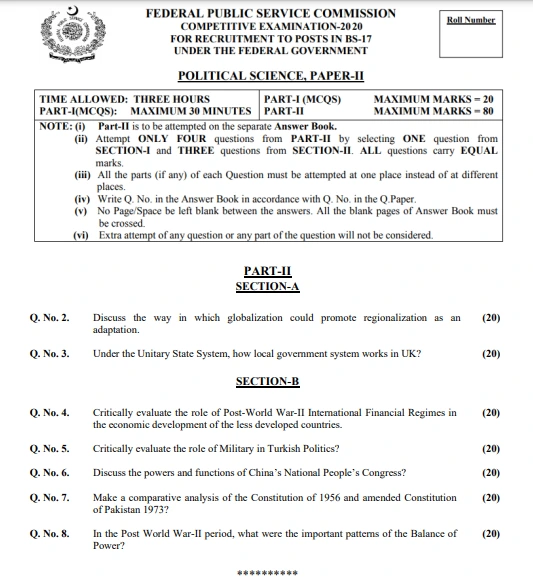
Q. No. 2. Discuss the way in which globalization could promote regionalization as an adaptation.
No. 3. Under the Unitary State System, how does the local government system work in the UK?
SECTION-B
Q. No. 4. Critically evaluate the role of Post-World War II International Financial Regimes in the economic development of the less developed countries.
Q. No. 5. Critically evaluate the role of the Military in Turkish Politics.
Q. No. 6. Discuss the powers and functions of China’s National People’s Congress.
Q. No. 7. Make a comparative analysis of the Constitution of 1956 and the amended Constitution of Pakistan 1973.
Q. No. 8. In the post-World War II period, what were the important patterns of the Balance of Power?
Summary
Q. No. 2. Discuss the way in which globalization could promote regionalization as an adaptation.
Summary: This question requires an analysis of how globalization, which connects the world economically, socially, and politically, can lead to regionalization. Globalization may encourage countries to form regional groups or organizations to address common challenges, such as economic integration, security concerns, and environmental issues. The question examines regionalization as a strategy for countries to adapt to global pressures by fostering closer cooperation and collaboration within specific regions, rather than on a global scale.
Q. No. 3. Under the Unitary State System, how does the local government system work in the UK?
Summary: This question explores the structure of local governance within a unitary state, specifically in the UK. A unitary state centralizes authority at the national level, with local governments operating under the power granted by the central government. The UK has a system of local authorities that manage services such as education, healthcare, and transportation, but their powers are subordinate to the central government. The question requires an understanding of how these local governments function and how their autonomy is regulated within the UK’s unitary framework.
Q. No. 4. Critically evaluate the role of Post-World War II International Financial Regimes in the economic development of the less developed countries.
Summary: This question asks for a critical evaluation of the impact that international financial institutions, such as the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the World Bank, have had on the economic development of less developed countries (LDCs) following World War II. These regimes aimed to stabilize global economies and promote growth in LDCs through financial aid and loans, but their policies and interventions have been subject to criticism for creating dependency, hindering true development, and promoting neoliberal reforms that may not always align with the needs of these countries.
Q. No. 5. Critically evaluate the role of the Military in Turkish Politics.
Summary: This question delves into the significant and often controversial role of the military in Turkish politics. The Turkish military has historically seen itself as the guardian of the secular state and has intervened in politics multiple times through coups and influencing civilian governance. The question requires an analysis of how the military’s influence has shaped Turkish political institutions, its relationship with political parties, and its impact on democracy, secularism, and civil-military relations in Turkey.
Q. No. 6. Discuss the powers and functions of China’s National People’s Congress.
Summary: This question explores the powers and functions of China’s National People’s Congress (NPC), the country’s highest legislative body. The NPC is responsible for enacting laws, approving the budget, and ratifying important government decisions. Despite being the largest legislative body in the world, its functions are primarily controlled by the Communist Party of China, making its role in governance more symbolic than substantive. The question requires a discussion of the NPC’s formal powers as well as its limited practical influence in the broader political structure of China.
Q. No. 7. Make a comparative analysis of the Constitution of 1956 and the amended Constitution of Pakistan 1973.
Summary: This question asks for a comparative analysis of the Constitution of Pakistan as it was established in 1956 and the amended Constitution of 1973. The 1956 Constitution was Pakistan’s first, and it established a parliamentary system but was eventually abrogated due to political instability. The 1973 Constitution, on the other hand, established a more stable framework, with key amendments and changes in governance, federalism, and the role of the president. This question invites a comparison of the key features, changes, and political implications of both documents.
Q. No. 8. In the post-World War II period, what were the important patterns of the Balance of Power?
Summary: This question requires an exploration of the changes in the global balance of power after World War II. The post-war period saw the emergence of the United States and the Soviet Union as superpowers, leading to the Cold War and the division of the world into opposing blocs. The question calls for a discussion of the key patterns in international relations, including alliances, military power, economic influence, and diplomacy that defined the balance of power in this era. It also invites an analysis of how these patterns shaped global politics and contributed to the geopolitical tensions during the Cold War.